InCellChem

Search
NameDescriptionContent
We Devoted Ourselves To The Development Of Biomedical Research Reagent.
Product Details
-

-
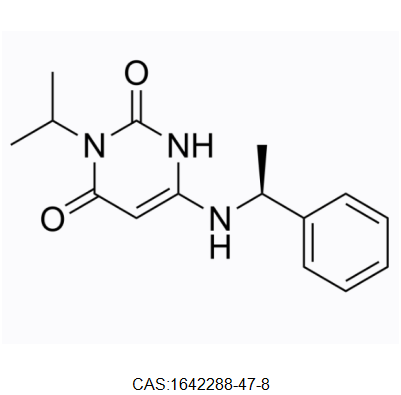
MYK-461,1642288-47-8,IC-0201470
MYK-461 is a small molecular chemical that reduces contractility by decreasing the adenosine triphosphatase activity of the cardiac myosin heavy chain.
MYK-461 reduced ATPase activity in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 value of 0.3 mM after treatment of mouse cardiac myofibrils. MYK-461 (>10 mM) decreased the maximal ATPase rate by ~90%. MYK-461 is active against both the A and B isoforms of cardiac myosin.
Treatment with MYK-461 decreased the rate of phosphate release in a dose-dependent manner without slowing adenosine diphosphate (ADP) release. MYK-461 decreases the myosin duty ratio and thus reduces the ensemble power, force and contractility produced by the sarcomere. Exposure to MYK-461 reduced maximal tension in a dose-dependent manner (~70% reduction at 1.0 mM) without altering the pCa50 or the tension at lower calcium concentrations.
MYK-461 showed a dose-dependent reduction in fractional shortening (IC50=0.18 mM) without changing the calcium transient after treated with adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. MYK-461 plasma exposures decreased fractional shortening in WT and mutant mice. Although MYK-461 inhibits the ATPase activity of skeletal myosin with a lower affinity (IC50 of 4.7 mM with rabbit skeletal myosin), treated rodents had no reduction in grip strength or voluntary exercise capacity. MYK-461 reduced cardiac contractility in a dose-dependent manner in normal and mutant mice without overt impairment of skeletal muscle function. MYK-461 was administered after the development of substantial hypertrophy, it did not significantly reduce the occurrence of fibrosis. Prehypertrophic R403Q mice treated with MYK-461 had 30% more aligned cardiomyocytes (59 ± 10%; P = 0.02).-
0.000.00
-
Discription
MYK-461 is a small molecular chemical that reduces contractility by decreasing the adenosine triphosphatase activity of the cardiac myosin heavy chain.
MYK-461 reduced ATPase activity in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 value of 0.3 mM after treatment of mouse cardiac myofibrils. MYK-461 (>10 mM) decreased the maximal ATPase rate by ~90%. MYK-461 is active against both the A and B isoforms of cardiac myosin.
Treatment with MYK-461 decreased the rate of phosphate release in a dose-dependent manner without slowing adenosine diphosphate (ADP) release. MYK-461 decreases the myosin duty ratio and thus reduces the ensemble power, force and contractility produced by the sarcomere. Exposure to MYK-461 reduced maximal tension in a dose-dependent manner (~70% reduction at 1.0 mM) without altering the pCa50 or the tension at lower calcium concentrations.
MYK-461 showed a dose-dependent reduction in fractional shortening (IC50=0.18 mM) without changing the calcium transient after treated with adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. MYK-461 plasma exposures decreased fractional shortening in WT and mutant mice. Although MYK-461 inhibits the ATPase activity of skeletal myosin with a lower affinity (IC50 of 4.7 mM with rabbit skeletal myosin), treated rodents had no reduction in grip strength or voluntary exercise capacity. MYK-461 reduced cardiac contractility in a dose-dependent manner in normal and mutant mice without overt impairment of skeletal muscle function. MYK-461 was administered after the development of substantial hypertrophy, it did not significantly reduce the occurrence of fibrosis. Prehypertrophic R403Q mice treated with MYK-461 had 30% more aligned cardiomyocytes (59 ± 10%; P = 0.02).
MYK-461 reduced ATPase activity in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 value of 0.3 mM after treatment of mouse cardiac myofibrils. MYK-461 (>10 mM) decreased the maximal ATPase rate by ~90%. MYK-461 is active against both the A and B isoforms of cardiac myosin.
Treatment with MYK-461 decreased the rate of phosphate release in a dose-dependent manner without slowing adenosine diphosphate (ADP) release. MYK-461 decreases the myosin duty ratio and thus reduces the ensemble power, force and contractility produced by the sarcomere. Exposure to MYK-461 reduced maximal tension in a dose-dependent manner (~70% reduction at 1.0 mM) without altering the pCa50 or the tension at lower calcium concentrations.
MYK-461 showed a dose-dependent reduction in fractional shortening (IC50=0.18 mM) without changing the calcium transient after treated with adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. MYK-461 plasma exposures decreased fractional shortening in WT and mutant mice. Although MYK-461 inhibits the ATPase activity of skeletal myosin with a lower affinity (IC50 of 4.7 mM with rabbit skeletal myosin), treated rodents had no reduction in grip strength or voluntary exercise capacity. MYK-461 reduced cardiac contractility in a dose-dependent manner in normal and mutant mice without overt impairment of skeletal muscle function. MYK-461 was administered after the development of substantial hypertrophy, it did not significantly reduce the occurrence of fibrosis. Prehypertrophic R403Q mice treated with MYK-461 had 30% more aligned cardiomyocytes (59 ± 10%; P = 0.02).
Copyright @ 2003-2024 InCellGene LLC.
InCellGene LLC.
FOLLOW US