InCellChem

Search
NameDescriptionContent
We Devoted Ourselves To The Development Of Biomedical Research Reagent.
Product Details
-

-
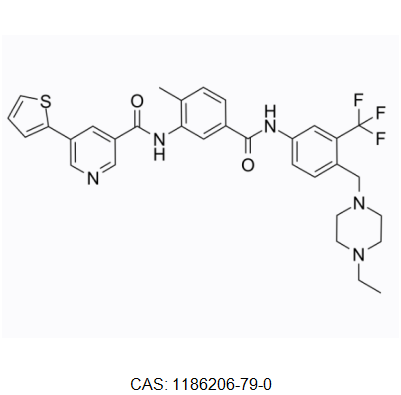
ALW-II-41-27,1186206-79-0,IC-0214889
ALW-II-41-27 is an Eph family tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 11 nM to inhibit Eph2[1].
ALW-II-41-27(1μM;72 h) inhibited the proliferation of Erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines and increased cell apoptosis. ALW-II-41-27 induced apoptosis was accompanied by an increase in caspase-3 and PARP and a decrease in the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-xL and MCL-1[3]. ALW-II-41-27(200, 600 or 1,000 nM ALW-II-41-27; 24, 48 or 72 h) inhibited cervical cancer (CC) cell proliferation, migration and invasion by blocking the RhoA/ROCK pathway[4]. ALW-II-41-27 inhibited pY772-EphA2 and EphA2-Y772A decreased the inhibitory effect of ALW-II-41-27 on NPC cell proliferation[6]. Combined treatment with ALW-II-41-27 plus cetuximab reverted primary and acquired resistance to cetuximab, causing cell growth inhibition, inducing apoptosis and cell-cycle G1-G2 arrest[7].
ALW-II-41-27(15 mg/kg;14 days; i.p.) significantly inhibited growth of the erlotinib-resistant tumors[3]. Administration of ALW-II-41-27(15, 30 mg/kg;twice a day; i.p.)significantly inhibited H358 tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice. Histological analysis showed a significant increase in apoptosis in tumors treated with ALW-II-41-27 compared with those treated with NG-25 or the carrier, similar to the effect of genetic ablation of EPHA2[2]. ALW-II-41-27 (12.5, 25, 50, and 100 μg/kg; i.p.) decreased gastrointestinal motility and abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores, markedly reduced the levels of oxidative stress markers [4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), protein carbonyl, and 8-hydroxy-2-de-axyguanine (8-OHdG)] and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and ICAM-1), and remarkably increased the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10) in serum and colon of Trichinella spiralis-infected mice[5].-
0.000.00
-
Discription
ALW-II-41-27 is an Eph family tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 11 nM to inhibit Eph2[1].
ALW-II-41-27(1μM;72 h) inhibited the proliferation of Erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines and increased cell apoptosis. ALW-II-41-27 induced apoptosis was accompanied by an increase in caspase-3 and PARP and a decrease in the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-xL and MCL-1[3]. ALW-II-41-27(200, 600 or 1,000 nM ALW-II-41-27; 24, 48 or 72 h) inhibited cervical cancer (CC) cell proliferation, migration and invasion by blocking the RhoA/ROCK pathway[4]. ALW-II-41-27 inhibited pY772-EphA2 and EphA2-Y772A decreased the inhibitory effect of ALW-II-41-27 on NPC cell proliferation[6]. Combined treatment with ALW-II-41-27 plus cetuximab reverted primary and acquired resistance to cetuximab, causing cell growth inhibition, inducing apoptosis and cell-cycle G1-G2 arrest[7].
ALW-II-41-27(15 mg/kg;14 days; i.p.) significantly inhibited growth of the erlotinib-resistant tumors[3]. Administration of ALW-II-41-27(15, 30 mg/kg;twice a day; i.p.)significantly inhibited H358 tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice. Histological analysis showed a significant increase in apoptosis in tumors treated with ALW-II-41-27 compared with those treated with NG-25 or the carrier, similar to the effect of genetic ablation of EPHA2[2]. ALW-II-41-27 (12.5, 25, 50, and 100 μg/kg; i.p.) decreased gastrointestinal motility and abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores, markedly reduced the levels of oxidative stress markers [4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), protein carbonyl, and 8-hydroxy-2-de-axyguanine (8-OHdG)] and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and ICAM-1), and remarkably increased the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10) in serum and colon of Trichinella spiralis-infected mice[5].
ALW-II-41-27(1μM;72 h) inhibited the proliferation of Erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines and increased cell apoptosis. ALW-II-41-27 induced apoptosis was accompanied by an increase in caspase-3 and PARP and a decrease in the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-xL and MCL-1[3]. ALW-II-41-27(200, 600 or 1,000 nM ALW-II-41-27; 24, 48 or 72 h) inhibited cervical cancer (CC) cell proliferation, migration and invasion by blocking the RhoA/ROCK pathway[4]. ALW-II-41-27 inhibited pY772-EphA2 and EphA2-Y772A decreased the inhibitory effect of ALW-II-41-27 on NPC cell proliferation[6]. Combined treatment with ALW-II-41-27 plus cetuximab reverted primary and acquired resistance to cetuximab, causing cell growth inhibition, inducing apoptosis and cell-cycle G1-G2 arrest[7].
ALW-II-41-27(15 mg/kg;14 days; i.p.) significantly inhibited growth of the erlotinib-resistant tumors[3]. Administration of ALW-II-41-27(15, 30 mg/kg;twice a day; i.p.)significantly inhibited H358 tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice. Histological analysis showed a significant increase in apoptosis in tumors treated with ALW-II-41-27 compared with those treated with NG-25 or the carrier, similar to the effect of genetic ablation of EPHA2[2]. ALW-II-41-27 (12.5, 25, 50, and 100 μg/kg; i.p.) decreased gastrointestinal motility and abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores, markedly reduced the levels of oxidative stress markers [4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), protein carbonyl, and 8-hydroxy-2-de-axyguanine (8-OHdG)] and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and ICAM-1), and remarkably increased the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10) in serum and colon of Trichinella spiralis-infected mice[5].
Copyright @ 2003-2024 InCellGene LLC.
InCellGene LLC.
FOLLOW US